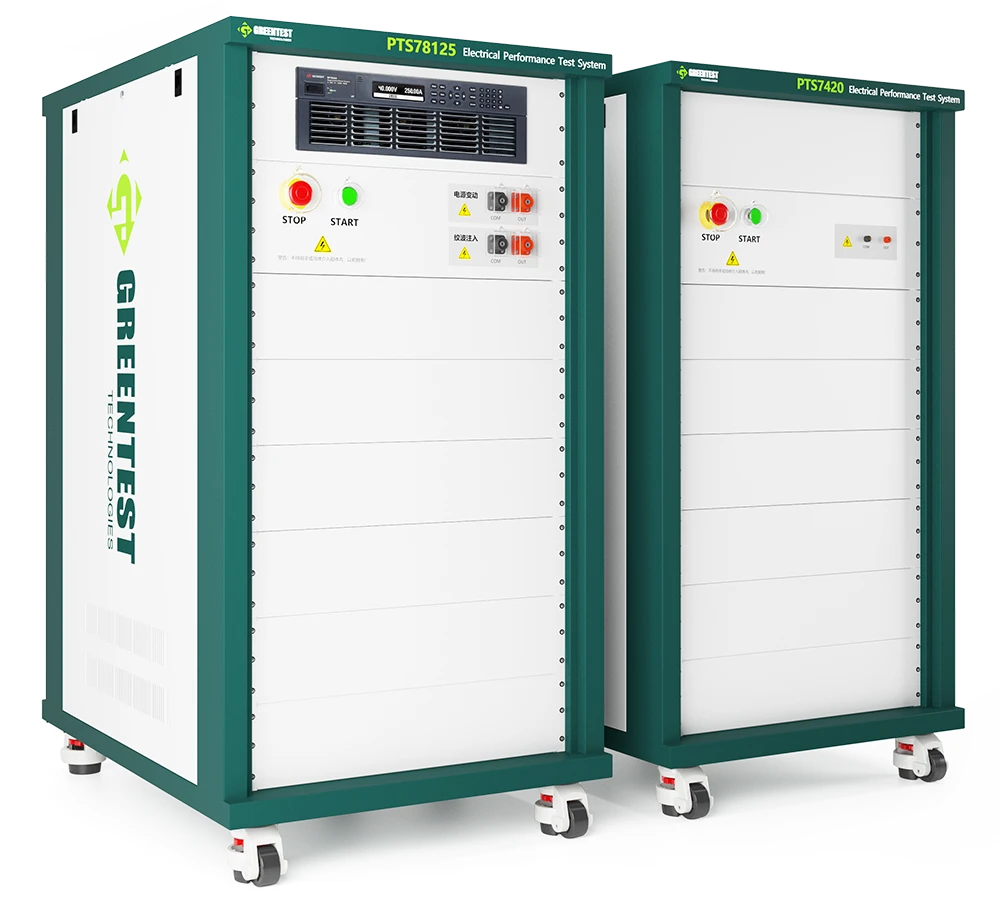
二、标准内容
2.1 适用范围
- 适用对象:标称电压为直流48V的道路车辆电气和电子部件(如DC/DC变换器、启动发电机)
- 排除范围:储能系统的电化学部分(仅其管理系统需测试)
- 车辆类型:涵盖乘用车、商用车及新能源专用作业车
2.2 电压范围定义
| 电压区间 | 范围 | 典型场景 | 允许持续时间 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 标称电压 | 36V≤U≤52V | 常规运行 | 持续 |
| 高暂压范围 | 52V<U≤54V | 校准存储介质、能量回收 | 短时 |
| 过压范围 | 54V<U≤58V | 电能回馈、控制错误 | 短时 |
| 高过压范围 | 58V<U≤60V | 控制错误 | |
| 低暂压范围 | 31V≤U<36V | 升压、冷启动 | 短时 |
| 欠压范围 | 24V≤U<31V | 冷启动 | 短时 |
| 低欠压范围 | 0V≤U<24V | 短期不连续供电、长期停车 |
2.3 功能状态分级体系
标准将部件功能状态分为5级,核心要求如下:
FS1
部件满足功能要求,性能无偏差,无性能降低或关机
FS2
部件功能要求,允许性能超出允差,不准许关机
FS3
部件无法功能要求,允许性能降低或关机。如果满足必要的运行条件,功能自动恢复,且性能恢复到规定的水平
FS4
部件无法满足功能要求,允许性能降低或关机。在车辆运行状态发生变化且满足必要的运行条件后,功能自动恢复,且性能恢复到规定的水平
FS5
部件功能失效,但不发生自燃。试验后,需修理或更换部件,才能继续使用
2.4 试验要点
| 测试项 | 直流 | 边沿特性 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 试验-01:标称电压范围 | 36-52V | 0.16V/ms | 需对DUT进行持续监控,直至测试循环结束; |
| 试验-02:低暂压范围和高暂压范围 | 31-36V | 0.5V/ms | 低暂压和高暂压测试各循环5次; |
| 试验-03:瞬时过电压 | 52-70V | 25.71V/ms |
1. 70V需持续40ms; 2. 试验循环次数1000次; |
| 试验-04:供电部件抛负载控制 | 52-70V | 25.71V/ms | 1. R=36Ω; 2. C=0.5mF; 3. 需100μs开关; 4. 实际的切换时间应在试验期间或试验前后进行测量; |
| 试验-05:启动特性 | 24-36V | 2.4V/ms | 需对DUT进行持续监控,直至测试循环结束; |
| 试验-06:长时过电压 | 52-60V | 80V/s | 需对DUT进行持续监控,直至测试循环结束; |
| 试验-07:可提供电能的耗能部件过电压 | 52-58V | 25V/ms | DUT的最大电压等级不应超过U1,从电压超过U2到电压低于U2的时间不应超过图12中的t1; |
| 试验-08:供电电压降低和升高 | 0-44V | 35mV/s | 需对DUT进行持续监控,直至测试循环结束; |
| 试验-09:电压纹波 | 31-54V |
/ | 1. 试验组合:需在不同电压点验证 f1:U0=35V和50V; f2:U0=34V和51V; f3:U0=32V和53V; 2. 频率及限值: f1:10Hz~1kHz,8Vpp/80App; f2:1kHz~30kHz,6Vpp/15App; f3:30kHz~200kHz,2Vpp/10App; 3. 试验分为参考试验和电压纹波试验; |
| 试验-10:复位特性 | 0-36V | ΔU1=2V ΔU2=0.5V |
在电压为U0时功能达到FS1。低于U0时,功能应符合表2要求。如果DUT进入FS4,则应在下一个电压骤降之前重新启动DUT; |
| 试验-11:短时中断供电 | 48V | / | 1. R1≤60mΩ; 2. 开关响应时间≤10μs; 3. 需进行两次参考测量再进行正式试验; |
| 试验-12:接地失效 | / | / | 1. 三重开关验证接地失效; 2. 需进行三部分试验: 第1部分:参考试验; 第2部分:GND48接地失效试验; 第3部分:GND12/24接地失效试验; |
| 试验-13:故障电流 | / | / | 1. 试验选项1:12V/24V和48V短路连接点(通信和I/O)之间流经的总电流应满足| I |≤10μA; 2. 试验选项2:12V/24V每个连接点(通信和I/O)和48V短路连接点(通信和I/O)之间流经的电流应满足| I |≤10μA; |
| 试验-14:接地偏移 | 36V,52V | / | 1. 试验布置分为选项1和选项2; 2. ±1V电位差不可影响DUT功能状态; |
| 试验-15:信号线和负载电路短路 | 36V,52V | / | 1. Zi1、Zi2≤0.02Ω; 2. 需针对四种条件进行试验: U0=36V,工作模式2.3; U0=52V,工作模式2.3; U0=36V,工作模式2.4; U0=52V,工作模式2.4; |
| 试验-16:静态电流 | 48V | / |
1. DUT根据是否具有周期性唤醒功能进行分类,且两者的测试时间t1不同; 2. 测试期间,DUT需保持休眠状态,电流测量以1Hz的频率测量不少于12h; |
2.5 附表:ISO 21780:2020 与 GB/T 45120-2024差异对比
| 标准号 | GB/T 45120-2024 | ISO 21780:2020 |
|---|---|---|
| 测试项 | 试验-14:接地偏移 | Test-14: ground offset |
| 试验时长 | 无规定 | t1=1min |
| 测试项 | 试验-16:静态电流 | Test-16: quiescent current |
| 测量时间 | 12h加最后一次唤醒周期结束的时长(有周期性唤醒功能的DUT) |
≥12h(无周期性唤醒功能的DUT) 12h加最后一次唤醒周期结束的时长(有周期性唤醒功能的DUT) |