应用解决方案
应用解决方案
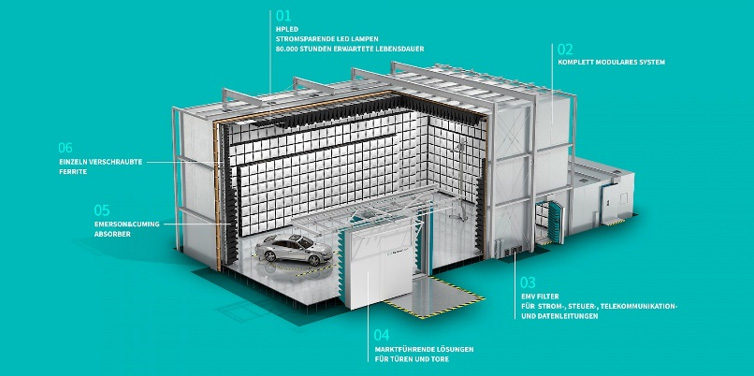
The fundamental components of an EMC anechoic chamber include an electromagnetic shield with a closed conductive frame, and electromagnetic wave-absorbing materials on the inner walls. The shield operates based on the principle of a Faraday cage, ensuring electromagnetic radiation cannot penetrate or escape the chamber. The electromagnetic wave-absorbing materials on the inner walls prevent reflection of test radiation, creating a comparable and constant testing environment.
Core Components of Anechoic Chamber:
Main steel structure, shield body, absorbing material, shielded door, filter, waveguide, lighting fixtures, interface panel, raised floor, antenna mast, turntable, monitoring system, smoke alarm system, and power distribution system
Primarily simulates free-space cosmic environments. Absorbing materials cover all six interior surfaces of the shielded structure to minimize all reflected waves (including diffracted and scattered waves). Mainly used for parameter measurements of microwave antenna systems (including base station antennas), Radar Cross-Section (RCS) measurement, electronic warfare simulation, and radiated spurious emissions testing.
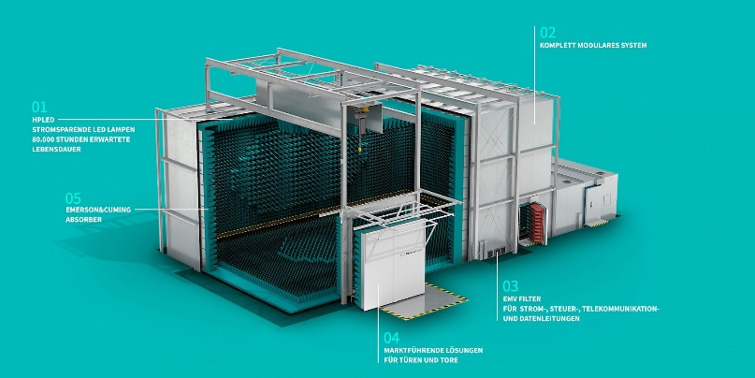
Features a metal reflective floor with absorbing materials on the other five surfaces, primarily simulating open-area test site conditions. Unaffected by weather or background noise, it serves as a widely adopted alternative to open-field testing. Mainly used for radiated emissions (EMI) and radiated immunity (EMS) measurements. Some radiated immunity tests may add absorbing materials to the floor to enhance field uniformity.